1.Identification
1.1 GHS Product identifier
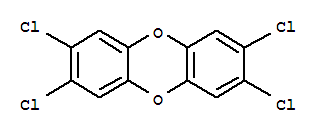
| Product name | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine |
|---|
1.2 Other means of identification
| Product number | - |
|---|---|
| Other names | Dibenzo[b,e][1,4]dioxin, 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro- |
1.3 Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use
| Identified uses | For industry use only. |
|---|---|
| Uses advised against | no data available |
1.4 Supplier's details
1.5 Emergency phone number
| Emergency phone number | - |
|---|---|
| Service hours | Monday to Friday, 9am-5pm (Standard time zone: UTC/GMT +8 hours). |
2.Hazard identification
2.1 Classification of the substance or mixture
Acute toxicity - Oral, Category 1
Eye irritation, Category 2
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, short-term (Acute) - Category Acute 1
Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term (Chronic) - Category Chronic 1
2.2 GHS label elements, including precautionary statements
| Pictogram(s) |   |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statement(s) | H300 Fatal if swallowed H319 Causes serious eye irritation H410 Very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects |
| Precautionary statement(s) | |
| Prevention | P264 Wash ... thoroughly after handling. P270 Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280 Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P273 Avoid release to the environment. |
| Response | P301+P310 IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER/doctor/… P321 Specific treatment (see ... on this label). P330 Rinse mouth. P305+P351+P338 IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. P337+P313 If eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P391 Collect spillage. |
| Storage | P405 Store locked up. |
| Disposal | P501 Dispose of contents/container to ... |
2.3 Other hazards which do not result in classification
none
3.Composition/information on ingredients
3.1 Substances
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine | 1746-01-6 | none | 100% |
4.First-aid measures
4.1 Description of necessary first-aid measures
General advice
Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance.
If inhaled
Fresh air, rest. Refer for medical attention.
In case of skin contact
Remove contaminated clothes. Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. Refer for medical attention .
In case of eye contact
First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then refer for medical attention.
If swallowed
Give a slurry of activated charcoal in water to drink. Induce vomiting (ONLY IN CONSCIOUS PERSONS!). Refer for medical attention .
4.2 Most important symptoms/effects, acute and delayed
Exposure Routes: inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact Symptoms: Irritation eyes; allergic dermatitis, chloracne; porphyria; gastrointestinal disturbance; possible reproductive, teratogenic effects Target Organs: Eyes, skin, liver, kidneys, reproductive system (NIOSH, 2016)
4.3 Indication of immediate medical attention and special treatment needed, if necessary
.../It was/ suggested that washing and/or tape stripping of the exposed area might remove most of the TCDD and reduce the potential for systemic exposure and toxicity since most of the TCDD remained within the horny stratum corneum layer of human skin even at 24 hr following exposure.
5.Fire-fighting measures
5.1 Extinguishing media
Suitable extinguishing media
Advice for firefighters: Wear self contained breathing apparatus for fire fighting if necessary.
5.2 Specific hazards arising from the chemical
Literature sources indicate that this chemical is nonflammable.
5.3 Special protective actions for fire-fighters
Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
6.Accidental release measures
6.1 Personal precautions, protective equipment and emergency procedures
Use personal protective equipment. Avoid dust formation. Avoid breathing vapours, mist or gas. Ensure adequate ventilation. Evacuate personnel to safe areas. Avoid breathing dust. For personal protection see section 8.
6.2 Environmental precautions
Evacuate danger area! Consult an expert! Personal protection: chemical protection suit including self-contained breathing apparatus.
6.3 Methods and materials for containment and cleaning up
... Studies show that ruthenium tetroxide can be used for detoxification of glassware and artifacts, and for the periodic purging of industrial reactors to counteract the accumulation of polychloro-p-dioxin residues. ...
7.Handling and storage
7.1 Precautions for safe handling
Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid formation of dust and aerosols. Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use.Provide appropriate exhaust ventilation at places where dust is formed. For precautions see section 2.2.
7.2 Conditions for safe storage, including any incompatibilities
Separated from food and feedstuffs.... Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins should be protected from light and kept at 4°C during transportation and storage.
8.Exposure controls/personal protection
8.1 Control parameters
Occupational Exposure limit values
NIOSH considers 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin to be a potential occupational carcinogen.
NIOSH usually recommends that occupational exposures to carcinogens be limited to the lowest feasible concentration.
Biological limit values
no data available
8.2 Appropriate engineering controls
Handle in accordance with good industrial hygiene and safety practice. Wash hands before breaks and at the end of workday.
8.3 Individual protection measures, such as personal protective equipment (PPE)
Eye/face protection
Safety glasses with side-shields conforming to EN166. Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
Skin protection
Wear impervious clothing. The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace. Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique(without touching glove's outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
Respiratory protection
Wear dust mask when handling large quantities.
Thermal hazards
no data available
9.Physical and chemical properties
| Physical state | PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION: White crystals or tan crystalline powder. |
|---|---|
| Colour | Colorless needles |
| Odour | no data available |
| Melting point/ freezing point | 295°C |
| Boiling point or initial boiling point and boiling range | Decomposes at 500°C |
| Flammability | Gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. |
| Lower and upper explosion limit / flammability limit | no data available |
| Flash point | 4°C (39 deg F) - closed cup |
| Auto-ignition temperature | no data available |
| Decomposition temperature | no data available |
| pH | no data available |
| Kinematic viscosity | no data available |
| Solubility | less than 1 mg/mL at 25°C |
| Partition coefficient n-octanol/water (log value) | log Kow = 6.8 |
| Vapour pressure | 6.4e-10 mm Hg at 20°C ; 0.0000000014 mm Hg at 25°C |
| Density and/or relative density | 1.8 g/cm3 |
| Relative vapour density | no data available |
| Particle characteristics | no data available |
10.Stability and reactivity
10.1 Reactivity
no data available
10.2 Chemical stability
Changed chemically when exposed in isooctane or n-octanol to UV light.
10.3 Possibility of hazardous reactions
2,3,7,8-TETRACHLORODIBENZO-P-DIOXIN (TCDD) reaacts when exposed to ultraviolet light in solution in isooctane or n-octanol. Undergoes catalytic perchlorination .
10.4 Conditions to avoid
no data available
10.5 Incompatible materials
This chemical is changed chemically when exposed as solutions in iso- octane or n-octanol to ultraviolet light. It undergoes catalytic perchlorination.
10.6 Hazardous decomposition products
/2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin/ begins to decompose at 500°C and virtually complete decomposition occurs within 21 seconds at a temp of 800°C.
11.Toxicological information
Acute toxicity
- Oral: LD50 Dog oral 1 ug/kg
- Inhalation: no data available
- Dermal: no data available
Skin corrosion/irritation
no data available
Serious eye damage/irritation
no data available
Respiratory or skin sensitization
no data available
Germ cell mutagenicity
no data available
Carcinogenicity
Evaluation: There is limited evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Overall Evaluation: 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin is carcinogenic to humans (Group 1). In making the overall evaluation, the Working Group took into consideration the following supporting evidence: (1) 2,3,7,8-TCDD is a multi-site carcinogen in experimental animals that has been shown by several lines of evidence to act through a mechanism involving the Ah receptor; (2) this receptor is highly conserved in an evolutionary sense and functions the same way in humans as in experimental animals; (3) tissue concentrations are similar in both heavily exposed human populations in which an increased overall cancer risk was observed and in rats exposed to carcinogenic dosage regimens in bioassays.
Reproductive toxicity
The results of available reproductive and developmental studies in humans are inconclusive. Animal studies have reported developmental effects, such as skeletal deformities, kidney defects, and weakened immune responses in the offspring of animals exposed to 2,3,7,8-TCDD during pregnancy. Reproductive effects, including altered levels of sex hormones, reduced production of sperm, and increased rates of miscarriages, have been seen in animals exposed to 2,3,7,8-TCDD.
STOT-single exposure
no data available
STOT-repeated exposure
no data available
Aspiration hazard
no data available
12.Ecological information
12.1 Toxicity
- Toxicity to fish: LD50; Species: Lepomis macrochirus (Bluegill); Concentration: 16 ug/kg /Conditions of bioassay not specified
- Toxicity to daphnia and other aquatic invertebrates: no data available
- Toxicity to algae: no data available
- Toxicity to microorganisms: no data available
12.2 Persistence and degradability
AEROBIC: In laboratory studies using aquatic sediments and lake water, TCDD was found to be recalcitrant to microbial attack(1). A 31-day aquatic model ecosystem study found C-14 labeled TCDD to be very stable to metabolism(2). To determine the persistence of TCDD, concentrations of 1, 10, and 100 ppm of unlabeled TCDD were added to 300 g samples of silty loam and sandy soils and then assayed periodically for chlorodibenzo-p-dioxin residues. Measurements of TCDD residues after 20, 40, 80, 160, and 350 days of incubation at 28°C in foil-sealed beakers indicated a relatively slow degradation process in both soils. After 350 days, 56% of the initially applied TCDD was recovered from the sandy soil, while 63% was recovered from the silty clay loam for all concentrations(3).
12.3 Bioaccumulative potential
Mean BCFs of 29,200 (dry weight) and 5,840 (wet weight) were measured for fathead minnows over a 28 day exposure(1); the elimination half-life after exposure was found to be 14.5 days(1). BCFs of approximately 1,585 to 3,311 were determined for rainbow trout and fathead minnow in laboratory flow-through studies during 4 to 5 exposures(2). The BCFs in several varieties of fish were 9,270-510,000 based on wet weight and 81,300-5,100,000 based on lipid weight(3). According to a classification scheme(4), BCF values of >1,000 for fish(1-3) suggest bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is very high(SRC). Several organisms were exposed in model ecosystem to C14-labeled TCDD for up to 31 days in an aquatic environment(5). TCDD accumulation was directly related to its concentration in water (0.05-1330 ng/L)(5); average concentrations were 2.0 to 2.6X10+4 (snail, gambusia and daphnid) and 4 to 9X10+3 (duckweed, algae, and catfish) times the concentration in water, and equilibrium concentrations were reached in tissues after 7 to 15 days(5). The BAF of TCDD in human fat has been reported as 115-740(3). After one month exposure to 0.81, 2.24 and 6.34 pg/g of TCDD in feed, the half-life of depletion in trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) was 1.6, 1.9 and 2.4 months, respectively(6). Log BAF values for TCDD in hardhead catfish (Ariopsis felis) (108 samples) and blue crab (Callinectes sapidus) (155 samples) sampled from the Houston Ship Channel, Texas were 6.68 and 6.7, respectively; samples were collected spring, summer and fall from 2002 to 2004(7). Biomagnification factors for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin were reported as 8.4 and 102 for dolphin/fish and dolphin/sediment; Hector's dolphin (Cephalorhynchus hectori), 8 species of fish and sediment sampled from the New Zealand coast(8). The mean BCF for vegetation/soil of TCDD was reported as 0.0147(9).
12.4 Mobility in soil
A mean log Koc of 7.39 was determined for ten contaminated soils from NJ and MO based on TCDD concentration in bulk soil and soil leachates(1). According to a classification scheme(2), this mean Koc value (2.45X10+7) suggests that TCDD is expected to be immobile in soil(SRC). TCDD dispersed only 10 cm from its initial position in soil plots at Eglin Air Force Base, Valparaiso, FL, observed over a 10 yr period (1972-1984)(3). TCDD remained in the upper 15 cm in soil cores collected from roadsides in Times Beach, MO in 1985 which had been sprayed with contaminated waste oils in the early 1970s(4). Tests conducted by the US Dept of Agric Pesticide Degradation Lab at Beltsville, MD determined that vertical movement of TCDD did not occur in a wide range of soil types(5). The mobility of TCDD in soil will increase if organic co-solvents that can solubilize TCDD are present in the soil(6).
12.5 Other adverse effects
no data available
13.Disposal considerations
13.1 Disposal methods
Product
The material can be disposed of by removal to a licensed chemical destruction plant or by controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing. Do not contaminate water, foodstuffs, feed or seed by storage or disposal. Do not discharge to sewer systems.
Contaminated packaging
Containers can be triply rinsed (or equivalent) and offered for recycling or reconditioning. Alternatively, the packaging can be punctured to make it unusable for other purposes and then be disposed of in a sanitary landfill. Controlled incineration with flue gas scrubbing is possible for combustible packaging materials.
14.Transport information
14.1 UN Number
| ADR/RID: UN2811 | IMDG: UN2811 | IATA: UN2811 |
14.2 UN Proper Shipping Name
| ADR/RID: TOXIC SOLID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. |
| IMDG: TOXIC SOLID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. |
| IATA: TOXIC SOLID, ORGANIC, N.O.S. |
14.3 Transport hazard class(es)
| ADR/RID: unknown | IMDG: unknown | IATA: unknown |
14.4 Packing group, if applicable
| ADR/RID: unknown | IMDG: unknown | IATA: unknown |
14.5 Environmental hazards
| ADR/RID: yes | IMDG: yes | IATA: yes |
14.6 Special precautions for user
no data available
14.7 Transport in bulk according to Annex II of MARPOL 73/78 and the IBC Code
no data available
15.Regulatory information
15.1 Safety, health and environmental regulations specific for the product in question
| Chemical name | Common names and synonyms | CAS number | EC number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxine | 1746-01-6 | none |
| European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances (EINECS) | Listed. | ||
| EC Inventory | Listed. | ||
| United States Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| China Catalog of Hazardous chemicals 2015 | Listed. | ||
| New Zealand Inventory of Chemicals (NZIoC) | Not Listed. | ||
| Philippines Inventory of Chemicals and Chemical Substances (PICCS) | Not Listed. | ||
| Vietnam National Chemical Inventory | Not Listed. | ||
| Chinese Chemical Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances (China IECSC) | Listed. | ||
16.Other information
Information on revision
| Creation Date | Aug 19, 2017 |
|---|---|
| Revision Date | Aug 19, 2017 |
Abbreviations and acronyms
- CAS: Chemical Abstracts Service
- ADR: European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road
- RID: Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail
- IMDG: International Maritime Dangerous Goods
- IATA: International Air Transportation Association
- TWA: Time Weighted Average
- STEL: Short term exposure limit
- LC50: Lethal Concentration 50%
- LD50: Lethal Dose 50%
- EC50: Effective Concentration 50%
References
- IPCS - The International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSC), website: http://www.ilo.org/dyn/icsc/showcard.home
- HSDB - Hazardous Substances Data Bank, website: https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/newtoxnet/hsdb.htm
- IARC - International Agency for Research on Cancer, website: http://www.iarc.fr/
- eChemPortal - The Global Portal to Information on Chemical Substances by OECD, website: http://www.echemportal.org/echemportal/index?pageID=0&request_locale=en
- CAMEO Chemicals, website: http://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/search/simple
- ChemIDplus, website: http://chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/chemidlite.jsp
- ERG - Emergency Response Guidebook by U.S. Department of Transportation, website: http://www.phmsa.dot.gov/hazmat/library/erg
- Germany GESTIS-database on hazard substance, website: http://www.dguv.de/ifa/gestis/gestis-stoffdatenbank/index-2.jsp
- ECHA - European Chemicals Agency, website: https://echa.europa.eu/


 F;
F; Xn
Xn